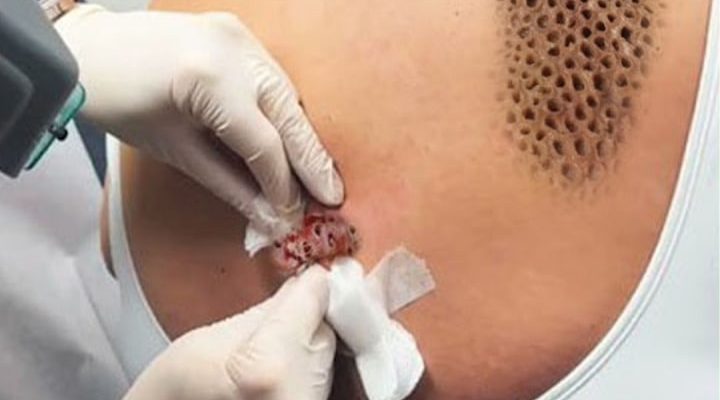
A skin abscess is a localized infection that results in a painful, swollen lump filled with pus. It usually develops when bacteria enter the skin through small cuts, wounds, or clogged hair follicles. The body’s immune system responds by sending white blood cells to fight the infection, which leads to the accumulation of pus beneath the skin. This collection of pus causes inflammation, redness, and tenderness in the affected area.
In the image above, a medical professional is performing a drainage procedure on a patient’s back. The patient has developed an abscess that required professional care. The doctor carefully opens the abscess using sterile tools and gently drains the infected material. This step is crucial to prevent the spread of bacteria and to relieve pressure and pain caused by the build-up of pus.
What Causes Skin Abscesses?
There are many reasons why a skin abscess can form. The most common causes include:
-
Bacterial infection, often due to Staphylococcus aureus.
-
Blocked sweat glands or hair follicles.
-
Ingrown hairs that trap bacteria under the skin.
-
Minor skin injuries such as cuts, insect bites, or puncture wounds.
-
Weakened immune systems, which make it harder for the body to fight infections.
Poor hygiene, excessive sweating, and friction from tight clothing can also increase the risk of developing an abscess.
Common Symptoms
An abscess typically begins as a small, firm bump that gradually enlarges over time. Symptoms may include:
-
Redness and swelling in the affected area.
-
Pain or tenderness when touched.
-
A visible accumulation of pus under the skin.
-
Warmth and throbbing sensation.
-
Fever or fatigue in more severe infections.
When the abscess matures, it may rupture on its own and drain pus, but it is always safer to have it medically treated to avoid complications.
The Treatment Process
The procedure, as seen in the image, is known as Incision and Drainage (I&D) — the standard method for abscess treatment.
-
Preparation: The area is cleaned and sterilized to minimize infection risk.
-
Incision: The doctor makes a small cut to allow pus to escape.
-
Drainage: Using gentle pressure and sterile gauze, the pus and debris are removed.
-
Cleaning: The wound is thoroughly cleaned with antiseptic solution.
-
Dressing: The area is covered with a clean bandage or gauze to protect it as it heals.
In some cases, a small piece of sterile gauze (wick) is placed inside the wound to keep it open for a short period, allowing any remaining pus to drain. The patient may be prescribed antibiotics to fight infection and pain relief medication to reduce discomfort.
Aftercare and Healing
Proper aftercare is essential for full recovery. Patients should:
-
Keep the wound clean and dry.
-
Change dressings as directed by the doctor.
-
Avoid touching or pressing the healing area.
-
Take all prescribed medications.
-
Return for follow-up visits to ensure the wound heals properly.
Healing time depends on the size and depth of the abscess, but most cases improve within 1–2 weeks.
Prevention Tips
To prevent future abscesses, it’s important to:
-
Maintain good personal hygiene.
-
Clean minor cuts and wounds promptly.
-
Avoid sharing razors, towels, or clothing.
-
Wear loose, breathable fabrics.
-
Strengthen the immune system with a balanced diet and enough rest.
Conclusion
A skin abscess may seem like a minor issue, but if left untreated, it can lead to serious infections and tissue damage. Early medical intervention is key to preventing complications. The procedure shown in the image demonstrates the importance of professional abscess drainage, where sterile techniques and proper wound care ensure safe healing and infection control.
If you notice a painful lump or swelling on your skin that doesn’t go away, consult a healthcare professional immediately. With proper care, you can recover quickly and restore the health of your skin.