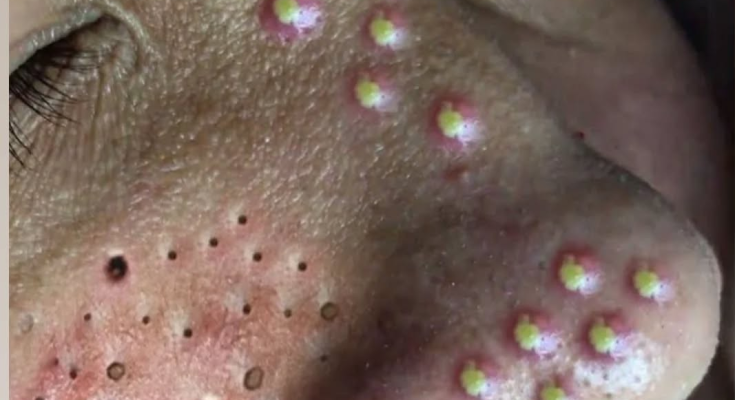
Acne is a widespread skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While blackheads are common, many individuals also struggle with whiteheads and inflamed pustules. The image above highlights clusters of white, pus-filled pimples along the nose and cheeks—signs of more severe acne that require careful attention and treatment.
What Are Whiteheads and Pustules?
Whiteheads are a type of closed comedone that form when pores become clogged with oil, bacteria, and dead skin cells. Unlike blackheads, they are covered by a thin layer of skin, trapping the contents inside. When inflammation develops, whiteheads can turn into pustules—red, swollen pimples filled with pus.
Why Do Whiteheads and Severe Acne Develop?
Several factors contribute to this type of acne:
-
Excess oil production – Sebaceous glands overproduce sebum, leading to clogged pores.
-
Bacterial growth – Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) bacteria thrive in blocked pores, causing infection.
-
Hormonal changes – Puberty, stress, or menstrual cycles often trigger flare-ups.
-
Poor skincare routine – Heavy, comedogenic products can worsen acne.
-
Lifestyle factors – Poor diet, dehydration, lack of sleep, and exposure to pollution may aggravate breakouts.
Effective Treatment Options
-
Topical Treatments
-
Benzoyl Peroxide – Reduces acne-causing bacteria and inflammation.
-
Salicylic Acid – Helps unclog pores and prevent new breakouts.
-
Topical Retinoids – Increase skin cell turnover, reducing blocked pores.
-
-
Oral Medications
-
Antibiotics – For moderate to severe cases, to reduce bacteria and inflammation.
-
Hormonal Therapy – Birth control pills or anti-androgens for hormonally driven acne.
-
Isotretinoin (Accutane) – A strong option for severe, resistant acne under medical supervision.
-
-
In-Clinic Treatments
-
Professional extractions.
-
Chemical peels to unclog pores and reduce scarring.
-
Laser or light therapy to target bacteria and reduce oil production.
-
Prevention Tips
-
Wash your face twice daily with a gentle cleanser.
-
Avoid picking or squeezing pimples to prevent scars and infections.
-
Use oil-free, non-comedogenic skincare and makeup.
-
Stay hydrated and eat a balanced diet with fewer processed foods.
-
Change pillowcases and towels regularly to avoid bacterial buildup.
Final Thoughts
Whiteheads and pustules can be painful and difficult to manage, but with proper care and treatment, acne can be controlled. For mild cases, consistent skincare and over-the-counter products may be enough. For more severe or persistent acne, consulting a dermatologist is the safest and most effective path toward clearer, healthier skin.