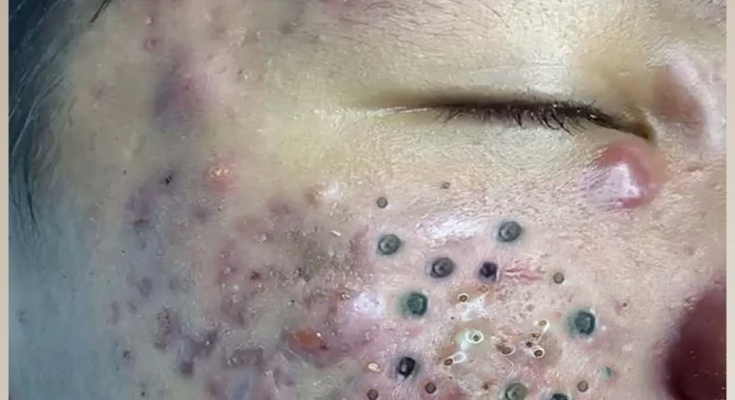
Acne is one of the most common skin conditions that affects millions of people worldwide, regardless of age or gender. However, in some individuals, acne can become more severe, leading to painful cysts, nodules, and deep inflammation that can cause both physical and emotional distress. The image above shows a case of severe acne characterized by inflamed pustules, cystic nodules, and dark comedones that cover a significant area of the cheek and forehead. Understanding the underlying causes and treatment options is essential for managing this condition effectively.
What is Severe Acne?
Severe acne, often referred to as cystic acne or nodulocystic acne, occurs when the hair follicles beneath the skin become clogged with oil (sebum), dead skin cells, and bacteria. Unlike mild or moderate acne, severe acne penetrates deeply into the skin, leading to larger, more painful lesions that may take weeks or months to heal. These lesions can form cysts — pus-filled lumps that cause redness, swelling, and discomfort.
The image depicts several visible signs of severe acne, including:
-
Cysts and nodules under the skin near the eyes and forehead.
-
Inflamed pustules and papules on the cheeks.
-
Dark comedones (blackheads) clustered in certain areas.
-
Redness and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, indicating both active and healing stages of acne.
Common Causes of Severe Acne
-
Hormonal Imbalance
Fluctuations in hormones, especially androgens, can lead to excessive sebum production. This is common during puberty, menstrual cycles, pregnancy, or conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). -
Bacterial Infection (Cutibacterium acnes)
This bacterium thrives in blocked hair follicles and contributes to inflammation, leading to pus formation and swelling. -
Genetics
If one or both parents have a history of severe acne, the chances of developing similar skin issues increase significantly. -
Poor Skincare Habits
Using harsh products, not cleansing properly, or over-exfoliating can irritate the skin and worsen breakouts. -
Diet and Lifestyle
High-glycemic foods, dairy products, stress, and lack of sleep can all contribute to increased oil production and inflammation. -
Environmental Factors
Exposure to pollution, humidity, or chemicals can clog pores and aggravate existing acne.
Possible Complications
Severe acne often leads to long-term complications if not treated properly:
-
Scarring: Deep cysts can rupture, damaging the skin and leading to permanent scars.
-
Hyperpigmentation: Dark spots remain even after acne heals.
-
Skin Infections: Open lesions may allow bacteria to enter and cause secondary infections.
-
Emotional Impact: Chronic acne can lower self-esteem and cause anxiety or depression.
Effective Treatment Options
Managing severe acne requires a comprehensive approach that includes medical, topical, and lifestyle interventions.
1. Dermatological Treatments
-
Oral Antibiotics: Help reduce inflammation and bacterial growth.
-
Isotretinoin (Accutane): A powerful medication prescribed for severe, resistant acne cases.
-
Hormonal Therapy: Birth control pills or anti-androgens like spironolactone can balance hormone levels.
-
Corticosteroid Injections: Reduce inflammation in large cysts and nodules.
2. Topical Medications
-
Retinoids (Tretinoin, Adapalene): Prevent clogged pores and promote cell turnover.
-
Benzoyl Peroxide: Kills bacteria and reduces oiliness.
-
Salicylic Acid: Helps exfoliate and unclog pores.
3. Professional Procedures
-
Chemical Peels: Improve skin texture and reduce scarring.
-
Laser and Light Therapy: Target acne-causing bacteria and reduce inflammation.
-
Drainage and Extraction: Safely remove large cysts under sterile conditions.
Home and Lifestyle Remedies
While medical treatment is essential, lifestyle changes can support the healing process:
-
Maintain a Gentle Skincare Routine: Cleanse twice daily with a mild, non-comedogenic cleanser.
-
Avoid Picking or Squeezing: This prevents scarring and bacterial spread.
-
Use Oil-Free Moisturizers: To keep the skin hydrated without clogging pores.
-
Eat a Balanced Diet: Focus on fruits, vegetables, and foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
-
Manage Stress: Practices such as meditation, yoga, and regular exercise help reduce hormonal triggers.
Preventing Recurrence
Once acne clears, maintaining results requires consistency and patience:
-
Continue using prescribed skincare products.
-
Schedule regular dermatology checkups.
-
Protect the skin from UV damage with sunscreen.
-
Keep makeup tools and pillowcases clean to minimize bacterial buildup.
Conclusion
Severe acne is more than just a cosmetic issue — it’s a complex skin condition that can affect overall well-being. With the right combination of medical treatment, proper skincare, and healthy habits, it’s possible to manage and even prevent future flare-ups. Early intervention by a dermatologist can make a significant difference, helping restore both clear skin and self-confidence.