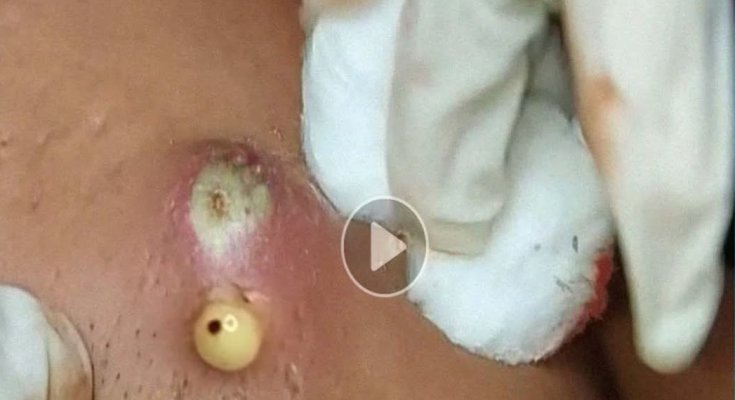
Skin abscesses and severe pus-filled infections are common skin problems that affect millions of people worldwide. The image above shows a classic example of a large, inflamed abscess undergoing professional drainage. This type of infection often results in visible swelling, redness, and a buildup of thick yellow pus beneath the skin. When not treated promptly, the infection can worsen and cause pain, fever, or even spread to deeper tissues.
In this comprehensive and SEO-friendly article, we explore what causes abscesses, how to manage them safely, the medical drainage process, aftercare, and prevention. Whether you’re creating educational content, writing for a health blog, or explaining dermatology procedures, this article serves as a complete resource.
What Is a Skin Abscess?
A skin abscess is a pocket of pus that forms under the skin due to a bacterial infection. It is often tender, warm, swollen, and painful. The body creates pus as a defense mechanism—your immune system sends white blood cells to attack the invading bacteria, which leads to a thick mixture of dead cells and microorganisms.
Key Characteristics of an Abscess
-
Red, painful bump
-
Warm skin surface
-
Visible white or yellow center
-
Swollen surrounding area
-
Fluid movement when touched
-
A “pointing” head as the pus collects
These features can be clearly seen in the provided image, where the abscess has risen to the surface and is actively draining.
Common Causes of Skin Abscesses
Understanding the root causes helps prevent future infections. Several factors contribute to abscess formation:
1. Bacterial Infection
The most common culprit is Staphylococcus aureus, including MRSA strains. Once bacteria enter through a break in the skin—whether a shaving nick, pimple, or insect bite—a painful infection may develop.
2. Blocked Pores or Hair Follicles
Clogged follicles trap oil, dirt, and bacteria, leading to:
-
Boils
-
Pimples that grow uncontrolled
-
Inflamed cyst-like lumps
3. Ingrown Hairs
When hair grows inward instead of outward, the immune system treats it like a foreign object. This triggers swelling and pus collection.
4. Poor Skin Hygiene
Sweat, dirt, and oil accumulation create a breeding ground for bacterial overgrowth.
5. Underlying Medical Conditions
Individuals with diabetes, weakened immune systems, or chronic skin problems are at higher risk.
6. Trauma or Friction
Tight clothing, rubbing, or pressure against the skin may break the surface, allowing bacteria to enter.
Early Signs and Symptoms of an Abscess
The symptoms typically worsen over time as the infection progresses. Common indicators include:
-
A firm, painful lump
-
Increasing redness and swelling
-
Heat over the area
-
White, yellow, or green center
-
Fluid buildup beneath the skin
-
Possible fever or chills
-
Skin sensitivity
If the abscess forms a visible “head,” it is close to rupturing or may require professional drainage.
Why Do Abscesses Fill With Pus?
Pus forms as the immune system fights infection. It contains:
-
White blood cells
-
Bacteria
-
Dead skin tissue
-
Protein-rich fluids
This mixture creates pressure in the abscess, making it painful. Draining the pus relieves the pressure and helps healing begin.
How Professional Abscess Drainage Works
Draining an abscess is a sterile medical procedure performed by trained professionals. It prevents the infection from spreading and reduces pain quickly.
Step-by-Step Overview
1. Cleaning the Surface
The skin is disinfected using antiseptic solutions to prevent further contamination.
2. Using Sterile Gloves
As seen in the image, gloved hands ensure a sterile environment.
3. Making a Small Incision
A medical blade or needle creates an opening to release pus.
4. Gentle Pressure
Controlled pressure pushes thick pus out. This is the stage clearly shown in your image—yellowish pus being extracted.
5. Flushing and Debridement
Any remaining pus or debris is removed from the cavity.
6. Applying Medication
Antibiotics or antiseptic dressings help prevent reinfection.
7. Bandaging the Wound
A sterile dressing protects the wound as it heals.
How Long Does an Abscess Take to Heal?
Healing time varies from a few days to a few weeks depending on:
-
Size of the abscess
-
Location
-
Depth of infection
-
Aftercare quality
Most people notice immediate pain relief after drainage.
What Happens If an Abscess Is Not Treated?
Leaving an abscess untreated can lead to serious problems:
-
Infection spreading to surrounding tissues (cellulitis)
-
Formation of multiple abscesses
-
Chronic skin damage
-
Bloodstream infection in severe cases
-
Permanent scarring
Early treatment is always recommended.
Home Remedies vs. Professional Care
Some small abscesses may improve with home care, while others require medical intervention.
Safe Home Treatments
-
Warm compresses
-
Gentle cleansing
-
Avoid squeezing or popping
-
Over-the-counter pain relief
When to Seek a Doctor
-
Abscess is large or deep
-
Severe pain
-
Fever
-
Pus is thick and persistent
-
Abscess keeps coming back
Prevention Tips: How to Avoid Future Abscesses
Preventing abscesses depends on maintaining clean, healthy skin and avoiding risky habits.
1. Practice Good Hygiene
Wash skin daily, especially areas prone to sweating.
2. Exfoliate Regularly
Clears dead skin and helps prevent clogged pores.
3. Avoid Squeezing Pimples
This often introduces bacteria deeper into the skin.
4. Clean Shaving Equipment
Razors can carry bacteria that cause infections.
5. Strengthen Your Immune System
Healthy lifestyle choices reduce infection risk.
6. Treat Minor Cuts Properly
Clean and cover wounds immediately.
Conclusion
Skin abscesses are painful, pus-filled infections that require proper care. The image you provided shows a realistic example of medical drainage, a crucial step in allowing the skin to heal. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options helps readers make informed decisions about their skin health. With proper hygiene, timely treatment, and attention to healing, abscesses can be managed safely and effectively.