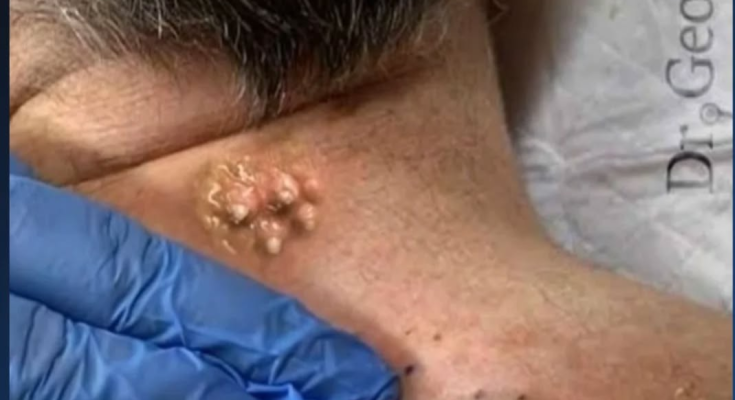
Skin lesions can appear in many shapes, sizes, and forms—ranging from benign cysts to clusters of clogged pores or nodular growths caused by chronic irritation or underlying dermatological conditions. The image presented shows a combination of several different skin abnormalities located on the back of the neck, an area prone to friction, sweat buildup, and oil accumulation. This article provides an in-depth overview of these lesions, why they form, how they are treated, and the importance of professional care.
1. Overview of What the Image Shows
The image highlights three distinct types of skin concerns:
1. A large cystic lesion being expressed
A gloved clinician is seen applying pressure to a sizeable, dome-shaped cyst. Its yellowish content suggests keratin, sebum, and inflammatory fluid, which are common materials found in:
-
Epidermoid cysts
-
Sebaceous cysts
-
Inflamed follicular cysts
These lesions often form when a hair follicle becomes blocked, trapping keratin under the skin. As they grow, they form a firm lump beneath the surface that may become painful or infected.
2. A cluster of raised nodules
Above the large cyst, there appears to be a group of small, flesh-colored to pink nodules. This formation is often seen in:
-
Sebaceous hyperplasia
-
Molluscum-like growths
-
Multiple small cysts
-
Chronic comedonal buildup
These bumps indicate overgrowth or blockage of sebaceous glands. Although often harmless, they can cause cosmetic concern and may occasionally become irritated.
3. A darkened area with multiple tiny pits or holes
On the right side of the neck, the image shows an unusual pattern: a group of small, dark, pore-like openings. This presentation may resemble:
-
Deep open comedones
-
Dilated pores of Winer
-
Scarred pores from chronic cystic acne
-
Clusters of oxidized sebum trapped in enlarged follicles
These pits can collect oil, dead skin cells, and debris, often leading to blackheads or chronic inflammation.
2. Causes Behind These Types of Skin Lesions
A. Sebaceous Cysts
These develop when the sebaceous gland or hair follicle becomes blocked. Contributing factors include:
-
Excessive oil production
-
Hormonal changes
-
Chronic friction (collar, helmet straps)
-
Poor skin hygiene
-
Previous skin injury or inflammation
B. Nodular Growths
Clusters of small bumps can form due to:
-
Overactive oil glands
-
Genetic predisposition
-
Viral or bacterial irritation
-
Chronic sun exposure
-
Long-standing comedonal acne
C. Deep Open Comedones or Pitted Lesions
These often result from:
-
Clogged pores left untreated
-
Long-term acne scarring
-
Oxidation of trapped sebum
-
Hormonal imbalance
-
Inadequate exfoliation
3. Symptoms and Risks
Skin lesions such as the ones shown may cause:
-
Pain or tenderness, especially in infected cysts
-
Swelling or redness
-
Discharge of foul-smelling material
-
Cosmetic concerns
-
Secondary infections if squeezed improperly
Large cysts can rupture internally, causing intense inflammation. Deep pitted comedones can reaccumulate debris, making them chronic.
4. Diagnosis
A dermatologist may diagnose these conditions through:
-
Visual examination
-
Palpation to assess depth and firmness
-
Dermatoscopy
-
Ultrasound for large or complex cysts
-
Biopsy if a growth appears unusual or atypical
Proper diagnosis ensures that lesions are benign and not mistaken for more serious conditions like skin tumors.
5. Treatment Options
1. Cyst Extraction or Surgical Removal
For large cysts like the one in the image, professional removal is often necessary. Steps typically include:
-
Sterilizing the area
-
Making a small incision
-
Expressing the contents
-
Removing the cyst wall (sac) to prevent recurrence
-
Closing or dressing the area
2. Extraction of Comedones
Deep blackheads or dilated pores may require:
-
Manual extraction
-
Use of comedone extractors
-
Chemical exfoliation (AHA/BHA)
-
Retinoid creams
3. Treatment of Sebaceous Hyperplasia or Nodular Bumps
Options include:
-
Cryotherapy
-
Electrocautery
-
Laser therapy
-
Topical retinoids
4. Preventive Care
-
Regular gentle exfoliation
-
Keeping the skin clean and dry
-
Avoiding harsh picking or squeezing
-
Using non-comedogenic products
-
Treating acne early
6. Healing and Aftercare
Following lesion removal, proper aftercare is essential:
-
Clean the area daily with mild antiseptic solution
-
Apply antibiotic ointment if advised
-
Avoid touching the wound
-
Keep the area protected from sun exposure
-
Watch for signs of infection (increasing redness, swelling, heat, pus)
Healing times vary from a few days for small extractions to several weeks for large cyst removals.
7. When to See a Doctor
You should seek medical attention if:
-
A cyst grows rapidly
-
Pain or redness increases
-
There is foul-smelling discharge
-
The lesion becomes warm or tender
-
You experience recurrent bumps in the same area
-
The appearance of the lesion changes unexpectedly
8. Final Thoughts
The image demonstrates how varied skin lesions can be—even within a small area of the body. From enlarged pores to clusters of nodules to a large inflamed cyst, each condition requires proper evaluation and treatment to prevent complications. Professional care is strongly recommended, as improper handling can lead to infection, scarring, and recurrence.
Understanding these lesions helps demystify what many people experience and empowers individuals to seek appropriate care when needed.