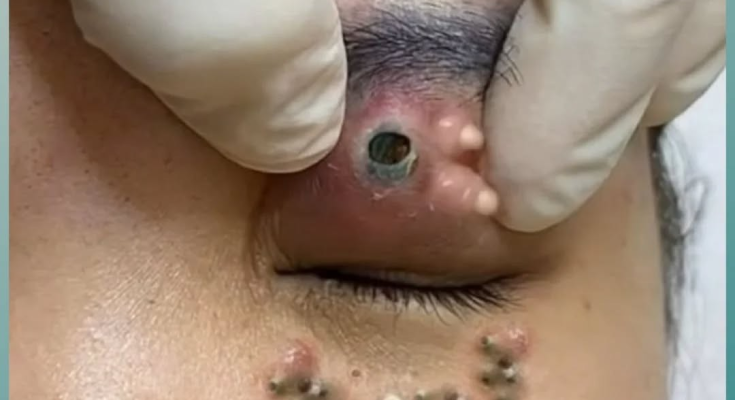
Skin lesions around the eyes and face can be alarming, especially when they appear suddenly or cause noticeable swelling, discoloration, or discharge. The image shows a cluster of lesions around the upper eyelid and cheek area, along with what appears to be an inflamed central opening on the eyelid surrounded by swollen, reddish skin. Several dark, raised spots appear on the cheek, forming a pattern that may indicate an underlying infection or inflammatory condition.
This type of presentation can happen due to various causes—ranging from bacterial infections and blocked glands to parasitic infestations or cyst formation. It is important to understand what these lesions might represent, how they develop, and what treatments are typically recommended.
What Are These Eyelid and Facial Lesions?
The lesions shown include:
1. Eyelid Swelling and Central Opening
The upper eyelid shows a swollen, inflamed bump with a central opening. This type of structure is often seen in:
-
Severe abscesses
-
Large infected cysts
-
Chalazion or hordeolum that has become secondarily infected
-
Complicated folliculitis
-
Parasitic burrows or extraction sites (in rare cases)
The surrounding skin is red and inflamed, indicating localized infection or accumulation of pus. The central hole could represent:
-
A drainage point created by pressure inside the lesion
-
A punctured cyst
-
A myiasis extraction site (fly larva removal), though this is rare and requires professional diagnosis
2. Multiple Dark Papules on the Cheek
The cheek area shows multiple tiny dark bumps arranged in a trail-like pattern. They resemble:
-
Crusts from healing pustules
-
Blackheads with surrounding inflammation
-
Dermal reaction from infection spreading along lymphatic pathways
-
Embedded debris or necrotic tissue within healing lesions
The clustered pattern suggests that they may be part of the same infectious or inflammatory process affecting the eyelid.
Possible Medical Conditions
1. Eyelid Abscess
An abscess forms when bacteria enter a blocked follicle or oil gland. The build-up of pus causes:
-
Pain
-
Redness
-
Swelling
-
Visible central pus pocket
The central opening in the image looks consistent with a draining abscess.
2. Severe Chalazion or Stye (Hordeolum)
If a blocked oil gland becomes infected, it can enlarge and rupture, creating an opening. When severe, the area becomes intensely red and swollen.
3. Cutaneous Myiasis (Rare)
This occurs when fly larvae infest the skin. Lesions often have a breathing hole, which may look similar to the opening seen in the image. This condition is more common in tropical or rural areas but requires confirmation by a medical professional.
4. Folliculitis or Nodular Acne
The darker bumps on the cheek may be clusters of infected pores or healing nodules.
5. Secondary Skin Infection
Multiple lesions on the cheek usually indicate:
-
Bacterial spread
-
Poor immune response
-
Delay in medical treatment
Symptoms You May Notice
People with similar lesions often report:
-
Pain or pressure around the eyelid
-
Swelling that affects vision
-
Pus drainage
-
Formation of multiple papules or pustules on the face
-
Itching or crawling sensations (in parasitic causes)
-
Fever, if the infection spreads deeper
Complications If Untreated
Because the eyelid and eye area are highly sensitive, ignoring these symptoms can lead to serious problems:
-
Worsening infection
-
Orbital cellulitis (infection spreading behind the eye)
-
Permanent scarring
-
Vision impairment
-
Spread of bacterial infection to the cheek or sinuses
Prompt professional care is essential.
Diagnosis
A medical professional may perform:
-
Physical examination
-
Dermatoscopy
-
Bacterial culture
-
Biopsy (if the cause is unclear)
-
Ultrasound of the eyelid lesion
-
Blood tests (to rule out systemic infection)
Treatment Options
1. Drainage of the Eyelid Lesion
If the bump contains pus, a doctor may:
-
Clean the area
-
Make a small incision
-
Allow fluid to drain
-
Prescribe antibiotics
This should never be attempted at home.
2. Antibiotics
Depending on the cause:
-
Topical antibiotics for mild bacterial infection
-
Oral antibiotics for deeper or spreading infections
-
Anti-parasitic medications if an infestation is confirmed
3. Warm Compresses
Before or after medical drainage, applying warm compresses can help reduce inflammation and promote natural drainage.
4. Proper Skin Hygiene
Cleaning the area regularly with mild antibacterial cleansers prevents recurrence.
5. Treatment of Cheek Lesions
Depending on severity, treatments may include:
-
Extraction of clogged pores
-
Topical antibiotics
-
Anti-inflammatory ointments
-
Chemical exfoliation to remove crusts
Prevention
To reduce the risk of similar lesions:
-
Avoid squeezing pimples or bumps near the eye
-
Maintain good facial hygiene
-
Use clean towels and pillowcases
-
Treat acne early to prevent deeper infections
-
Seek medical attention for any rapidly growing or painful eyelid bump
When to See a Doctor
Seek immediate care if you notice:
-
Increasing swelling
-
Vision changes
-
Fever
-
Pain that worsens
-
Pus or foul-smelling discharge
-
Lesions spreading across the face
Early treatment prevents complications and speeds recovery.
Conclusion
The type of eyelid and facial lesions shown in the image is a sign of a significant underlying skin issue—whether bacterial, inflammatory, or parasitic. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and available treatments is essential for protecting both eye health and overall skin integrity. Anyone experiencing similar symptoms should seek professional medical assistance promptly to ensure safe and effective treatment.