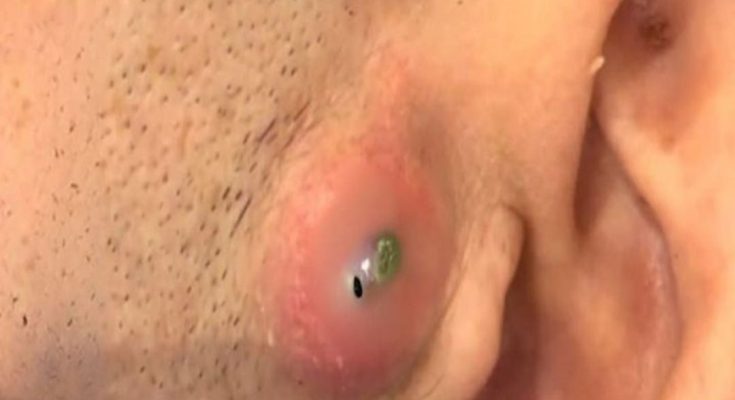
Abscesses on the face can be extremely painful, alarming to look at, and difficult to manage without proper medical care. The image above shows a large, swollen abscess located just beside the ear, with visible greenish pus beneath the skin—a sign of active infection. This kind of swelling often develops rapidly, causing discomfort, tenderness, and pressure as the abscess fills with infected material.
This article provides an in-depth explanation of what a facial abscess is, why it forms, common symptoms, complications, and how it is treated both medically and at home.
What Is a Facial Abscess?
A facial abscess is a localized collection of pus beneath the skin, resulting from an infection. It usually appears as a red, swollen, warm, and painful lump, which may develop a white or yellow “head” as the pus moves closer to the skin’s surface.
Abscesses occur when bacteria—commonly Staphylococcus aureus—enter the skin through a small break such as:
-
An ingrown hair
-
A clogged pore
-
A small cut or scratch
-
A pimple that becomes infected
-
Shaving irritation
-
A blocked sebaceous gland
Once bacteria invade, the immune system sends white blood cells to fight the infection, producing pus, which contains bacteria, dead cells, and inflammatory debris.
Signs and Symptoms of a Facial Abscess
In the image, the swelling near the ear shows classic signs of an abscess. These include:
1. Redness and Swelling
The skin appears stretched, shiny, and inflamed due to the buildup of pressure inside the abscess.
2. Pain and Tenderness
Abscesses are often extremely tender, especially when touched. Pain may radiate to surrounding areas such as the jaw, neck, or ear.
3. Visible Pus Under the Skin
The greenish-yellow area indicates accumulated pus, which can be a sign of advanced infection.
4. Warmth Over the Affected Area
Inflamed tissue typically feels warm due to increased blood flow.
5. A Central “Head” Forming
The small, darker opening in the swollen lump may indicate that the abscess is close to rupturing.
6. Fever or Malaise (In Severe Cases)
Body-wide symptoms can arise if the infection spreads.
Common Causes of Abscesses Near the Ear
Abscesses in this location can develop due to:
1. Infected Sebaceous (Oil) Glands
When an oil gland becomes blocked, bacteria may multiply inside, forming a cyst that can later turn into an abscess.
2. Pimple or Acne Infection
A deep pimple may become infected if it is squeezed or irritated.
3. Ingrown Hair or Folliculitis
Hair follicles in the beard area can easily become infected from shaving.
4. Trauma or Skin Damage
Small cuts, scratch marks, or insect bites can allow bacteria to enter the skin.
5. Otitis Externa or Ear Infection Spread
In rare cases, an infection from the ear canal can extend into the surrounding tissue.
Potential Complications If Left Untreated
Facial abscesses, especially near sensitive areas like the ear and jaw, should not be ignored. Complications may include:
-
Spread of infection to deeper tissues
-
Formation of multiple pockets of pus (cellulitis or phlegmon)
-
Scarring after healing
-
Spread to lymph nodes (lymphadenitis)
-
Systemic infection
Because the face contains many blood vessels that connect to deeper structures, untreated abscesses can, in very rare cases, lead to more serious issues.
Treatment Options for a Facial Abscess
Treatment depends on the size, location, and severity of the infection. The abscess in the image appears large and filled with pus, making medical drainage the most effective solution.
1. Warm Compresses
Applying warm compresses several times a day can help increase blood flow and encourage the abscess to come to a head.
2. Medical Incision and Drainage (I&D)
For large or painful abscesses, a healthcare professional will:
-
Numb the area
-
Make a small incision
-
Drain the pus completely
-
Clean the cavity
-
Sometimes place a small wick to allow continued drainage
This procedure provides almost immediate relief.
3. Antibiotics
Doctors may prescribe antibiotics if:
-
The abscess is large
-
There is spreading redness
-
The patient has fever
-
The infection is complicated
Common antibiotics include cephalexin, clindamycin, or doxycycline (depending on bacterial resistance patterns).
4. Avoid Squeezing or Popping
Trying to pop an abscess at home can push the infection deeper, worsen inflammation, or cause scarring.
Home Care After Treatment
Once drained, proper aftercare is essential:
-
Keep the area clean and covered
-
Change dressings daily
-
Continue prescribed antibiotics until completion
-
Avoid touching or squeezing the area
-
Watch for recurring swelling or redness
Healing typically takes several days to a week.
When to See a Doctor Immediately
Seek medical attention if:
-
The abscess becomes extremely painful
-
Red streaks appear
-
You develop fever
-
The swelling spreads
-
The abscess does not drain
-
There is recurrent infection
Facial abscesses should always be taken seriously due to their proximity to vital structures.
Conclusion
The abscess shown in the image is a significant, inflamed lesion indicating bacterial infection and accumulation of pus. While it may look alarming, proper medical treatment—especially drainage—can resolve it quickly and safely. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments helps prevent complications and ensures fast recovery.