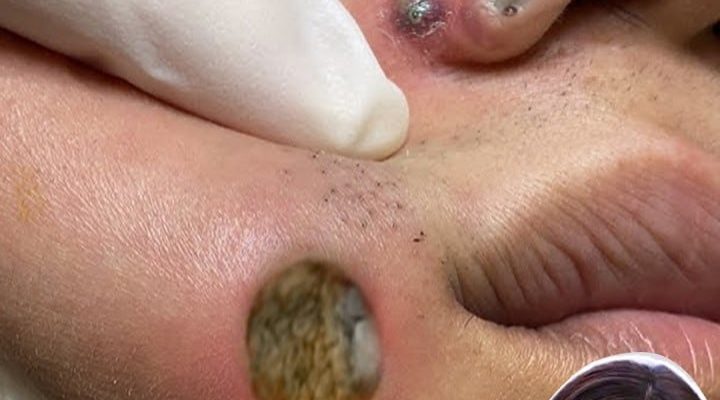
Facial skin lesions can range from mild acne to severe inflammatory conditions that require medical attention. The image presented shows a large crusted lesion with surrounding redness and swelling, accompanied by a smaller inflamed pustule nearby. These visual signs suggest an advanced skin infection or poorly healed inflammatory lesion. Understanding the causes, risks, and correct management of such conditions is essential to prevent complications such as scarring, tissue damage, or systemic infection.
1. What Is a Crusted Facial Lesion?
A crusted lesion forms when damaged skin produces exudate—a mixture of pus, blood, and inflammatory fluid—that dries and hardens on the surface. This process often occurs after:
-
Severe acne
-
Abscess formation
-
Improper pimple extraction
-
Bacterial skin infections
-
Trauma or repeated picking
The thick, yellow-brown crust seen in the image suggests ongoing inflammation beneath the surface, rather than a fully healed wound.
2. Surrounding Redness and Swelling: Signs of Active Infection
The redness (erythema) and swelling around the lesion indicate that the immune system is actively fighting infection. This response is commonly associated with:
-
Bacterial invasion, often Staphylococcus aureus
-
Blocked sebaceous glands
-
Deep follicular infection
-
Abscess development
When the skin becomes warm, tender, and swollen, it signals that the infection may be spreading beyond the original pore or follicle.
3. Nearby Pustules: A Warning Sign
The presence of a smaller pustule near the main lesion suggests that the infection may be spreading locally. This can happen when:
-
Bacteria travel through surrounding hair follicles
-
Pressure is applied during squeezing
-
Skin barriers are broken repeatedly
-
Hygiene practices are inadequate
Multiple lesions in close proximity often indicate that self-treatment has worsened the condition.
4. Common Conditions Associated with This Presentation
A. Infected Acne (Severe Acne Vulgaris)
Deep nodular or cystic acne can rupture beneath the skin, causing crusting and inflammation.
B. Skin Abscess
An abscess is a pocket of pus trapped beneath the skin, often requiring professional drainage.
C. Impetiginized Lesions
Open acne wounds can become secondarily infected, forming thick honey-colored crusts.
D. Folliculitis Progressing to Furuncle
An infected hair follicle may enlarge and deepen, becoming painful and crusted.
5. The Dangers of Squeezing and Manual Extraction
The image shows pressure being applied to inflamed facial skin—a practice that carries significant risks:
❗ Deeper Infection
Squeezing pushes bacteria further into tissue.
❗ Permanent Scarring
Inflammation disrupts collagen production.
❗ Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation
Dark marks may persist for months or years.
❗ Spread of Infection
Particularly dangerous on the face, where veins connect to deeper structures.
This is especially critical in the facial “danger zone”, which includes the nose, cheeks, and upper lip.
6. Proper Management and Treatment
Immediate Care
✔ Keep the area clean and dry
✔ Avoid touching or picking
✔ Use sterile saline or gentle cleansers
✔ Apply warm compresses to encourage drainage
Medical Treatments
A healthcare professional may recommend:
-
Topical or oral antibiotics
-
Antibacterial ointments
-
Professional drainage under sterile conditions
-
Anti-inflammatory medications
Self-treatment with sharp tools or excessive pressure should be strictly avoided.
7. Healing and Recovery Process
Properly treated lesions will:
-
Gradually reduce redness
-
Lose crust thickness
-
Close from the edges inward
-
Leave minimal scarring
Improperly treated lesions may worsen, deepen, or form chronic scars.
8. Prevention of Severe Facial Lesions
To reduce recurrence:
-
Maintain consistent facial hygiene
-
Use non-comedogenic skincare products
-
Avoid aggressive exfoliation
-
Clean makeup tools regularly
-
Do not squeeze pimples
-
Seek early treatment for inflamed acne
9. When to Seek Medical Attention
Consult a doctor immediately if:
-
The lesion grows rapidly
-
Pain increases significantly
-
Fever develops
-
Redness spreads outward
-
Pus continues to accumulate
-
Vision or facial movement is affected
Early medical intervention can prevent serious complications.
Conclusion
The image illustrates a severely inflamed, crusted facial lesion with active infection, likely worsened by manual manipulation. While facial skin conditions are common, severe presentations require professional care. Attempting to squeeze or treat such lesions at home often leads to scarring, prolonged healing, and spread of infection.
Healthy skin depends on patience, hygiene, and proper medical guidance, especially when dealing with advanced or painful lesions.