Introduction
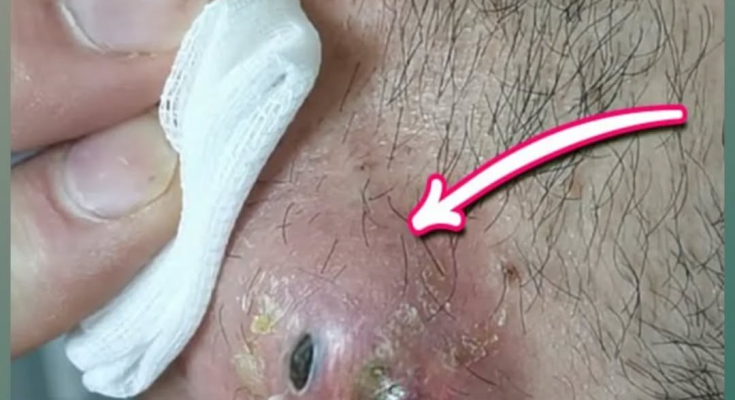
Facial skin abscesses are painful, localized infections that can develop beneath the surface of the skin. They are commonly filled with pus and caused by bacterial infection. The image above shows a facial abscess located in the beard area, characterized by redness, swelling, pus drainage, and surrounding inflammation. Abscesses in this region are particularly concerning due to the rich blood supply of the face and the potential risk of spreading infection if not treated properly.
This article provides an in-depth explanation of facial abscesses, focusing on causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, complications, and prevention, especially when they occur near facial hair follicles.
What Is a Facial Abscess?
A facial abscess is a collection of pus trapped under the skin caused by infection. It develops when bacteria enter the skin through small cuts, ingrown hairs, acne lesions, or shaving-related trauma. The immune system responds by sending white blood cells to fight the infection, leading to tissue breakdown and pus formation.
In the image, the abscess appears inflamed, with visible pus drainage, crusting, and surrounding redness—classic signs of an active bacterial infection.
Common Causes of Facial Abscesses
1. Infected Hair Follicles (Folliculitis)
Facial hair areas, especially the beard, are prone to folliculitis, which can progress into a deeper abscess if untreated.
2. Ingrown Hairs
Shaving can cause hair to curl back into the skin, leading to inflammation and bacterial infection.
3. Acne Infections
Severe acne lesions may rupture under the skin and become infected, forming an abscess.
4. Poor Shaving Hygiene
Using unclean razors or shaving against the grain increases the risk of skin trauma and infection.
5. Bacterial Infection
The most common culprit is Staphylococcus aureus, including methicillin-resistant strains (MRSA).
6. Weakened Immune System
People with diabetes, chronic illness, or weakened immunity are more prone to abscess formation.
Signs and Symptoms
Facial abscesses often present with the following symptoms:
-
Painful, swollen lump under the skin
-
Redness and warmth around the affected area
-
Visible pus or fluid drainage
-
Shiny, stretched skin over the abscess
-
Crusting or scab formation
-
Fever (in severe cases)
-
Tenderness when touched
In the image, the abscess shows active drainage, thick pus, and surrounding inflamed tissue, indicating a mature abscess that has either ruptured or been partially drained.
Why Facial Abscesses Are Serious
The face contains an area known as the “danger triangle”, which includes the nose, upper lip, and nearby regions. Infections here can, in rare cases, spread to deeper structures such as:
-
Blood vessels
-
Sinuses
-
Brain (via cavernous sinus thrombosis)
Because of these risks, facial abscesses should never be ignored or aggressively squeezed at home.
Diagnosis
A healthcare provider usually diagnoses a facial abscess through:
-
Visual examination
-
Palpation to assess depth and tenderness
-
Pus culture (if infection is severe or recurrent)
-
Blood tests (in complicated cases)
Treatment Options
1. Incision and Drainage (I&D)
This is the most effective treatment for a mature abscess. A small sterile incision allows pus to drain, relieving pain and pressure.
Important: Abscesses should never be drained at home, especially on the face.
2. Antibiotic Therapy
Oral or topical antibiotics may be prescribed, especially if:
-
The abscess is large
-
There is surrounding cellulitis
-
The patient has fever or immune compromise
3. Warm Compresses
Applying warm compresses helps increase blood flow and may encourage natural drainage in early stages.
4. Proper Wound Care
-
Keep the area clean and dry
-
Use sterile dressings
-
Avoid shaving over the affected area
Possible Complications
If untreated or improperly managed, facial abscesses can lead to:
-
Spread of infection (cellulitis)
-
Scarring
-
Recurrent abscess formation
-
Bloodstream infection (sepsis)
-
Facial nerve involvement
-
Rare intracranial infection
Healing Process and Recovery
After proper drainage and treatment:
-
Pain typically improves within 24–48 hours
-
Swelling gradually reduces over several days
-
Complete healing may take 1–2 weeks
-
Mild scarring may remain
Following medical advice closely reduces the risk of recurrence.
Prevention Tips
To reduce the risk of facial abscesses:
-
Use clean, sharp razors
-
Shave in the direction of hair growth
-
Cleanse the face daily
-
Avoid picking or squeezing acne
-
Treat ingrown hairs early
-
Maintain good personal hygiene
-
Manage underlying health conditions like diabetes
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical attention immediately if:
-
The abscess is on the face
-
Pain and swelling worsen
-
Fever develops
-
Pus continues to drain
-
Redness spreads rapidly
-
The abscess keeps coming back
Conclusion
Facial abscesses, particularly in the beard area, are painful and potentially serious skin infections. The image clearly demonstrates the classic features of a mature abscess, including pus accumulation and inflammation. Early recognition, professional medical treatment, and proper hygiene are essential to prevent complications and ensure safe healing.
Never attempt to squeeze or drain a facial abscess at home. Prompt care not only speeds recovery but also protects against dangerous spread of infection.