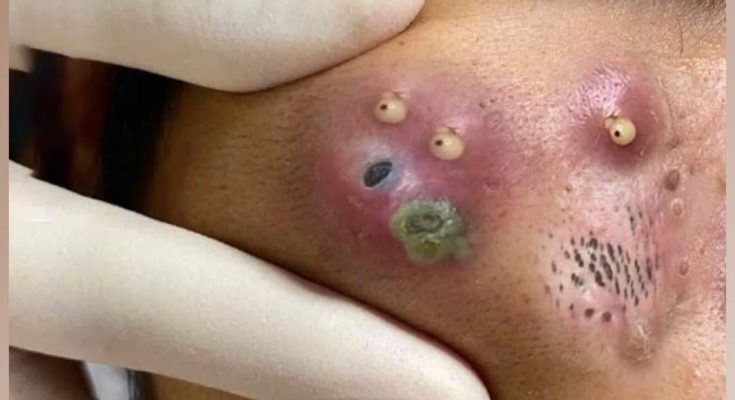
Skin abscesses and severe pimples on the face are not just cosmetic concerns — they are signs of deeper skin infections that can become painful and potentially dangerous if left untreated. The image above captures a severe case of multiple abscesses forming on the cheek, each filled with pus and surrounded by inflamed, swollen skin. It serves as a vivid example of how bacterial infections can progress beneath the surface, leading to painful lumps that require medical attention and professional extraction.
What is a Facial Abscess?
A facial abscess is a pocket of pus that develops under the skin due to infection. It often begins with a clogged pore or follicle that traps bacteria, dead skin cells, and oil inside. When the body’s immune system detects this invasion, it sends white blood cells to fight the infection — resulting in inflammation, swelling, redness, and the formation of pus.
Unlike simple acne, an abscess usually involves a deeper infection that can spread rapidly to surrounding tissues. This makes it more severe and more painful. In the image, multiple abscesses have formed close together, indicating a cluster infection possibly caused by Staphylococcus aureus, one of the most common bacteria responsible for skin infections.
Possible Causes of Severe Skin Infection
Several factors can contribute to the development of severe abscesses like the one shown:
-
Poor hygiene or bacterial contamination: When bacteria enter clogged pores or minor skin injuries, they can multiply quickly.
-
Untreated or improperly managed acne: Deep cystic acne can evolve into abscesses if left unattended or repeatedly squeezed.
-
Ingrown hairs: Facial hair, especially around the beard or cheek area, can sometimes curl inward and create an infected bump.
-
Weak immune system: People with compromised immune systems are more prone to skin infections.
-
Use of unclean tools: Non-sterile extraction tools, razors, or makeup brushes can introduce harmful bacteria to the skin.
Symptoms and Progression
A developing abscess typically starts as a small, tender bump that gradually grows in size. As infection progresses, the area becomes more painful, red, and warm to the touch. Eventually, pus accumulates under the surface, creating visible white or yellow heads, as seen in the image. Some abscesses may even turn green or black due to necrotic tissue, which indicates dead cells caused by bacterial destruction.
In this particular case, the cheek shows multiple raised pustules with distinct white heads and an area of dark-green discoloration, suggesting both infection and partial tissue damage. The swelling around the lesions shows that the infection has extended deeper beneath the skin.
The Extraction and Drainage Procedure
When an abscess reaches this stage, medical extraction becomes necessary. The procedure is typically performed under sterile conditions by a dermatologist or trained medical professional. The steps often include:
-
Cleansing the area with antiseptic to prevent further bacterial spread.
-
Applying local anesthesia to minimize pain during the procedure.
-
Making a small incision or applying pressure to release the pus and debris inside.
-
Draining the abscess completely, ensuring that all infected material is removed.
-
Cleaning and dressing the wound to promote healing and prevent reinfection.
In some cases, antibiotic ointments or oral medications are prescribed afterward to fight any lingering bacteria. The patient must follow up with wound care instructions, including keeping the area clean and avoiding the use of harsh skincare products.
Aftercare and Healing Process
Post-extraction care plays a crucial role in recovery. The skin must be kept clean and dry, and any prescribed medication should be used consistently. Common aftercare tips include:
-
Washing the area gently with mild soap and water.
-
Applying prescribed antibiotic creams or healing ointments.
-
Avoiding touching or picking at the healing site.
-
Using a clean towel and pillowcase to prevent reinfection.
-
Staying hydrated and maintaining a balanced diet to support immune response.
Within a few days, the swelling and redness typically begin to subside. However, in severe cases like this, complete healing may take a few weeks, and scarring can occur if the infection penetrated deep into the dermal layers.
Preventing Future Abscesses
Prevention is always better than treatment. Here are a few ways to avoid developing severe abscesses:
-
Maintain proper facial hygiene — wash your face regularly and avoid oily or dirty environments.
-
Never squeeze pimples with unclean hands or tools.
-
Disinfect razors, tweezers, and other skincare equipment before and after each use.
-
Exfoliate the skin gently to prevent clogged pores.
-
Seek early medical help for persistent acne or painful bumps.
Conclusion
This case of severe facial abscess extraction highlights the importance of timely and professional skin care. What might begin as a simple pimple can escalate into a serious infection requiring drainage and antibiotics. Professional treatment not only removes the infection but also helps preserve the skin’s natural structure and reduce the risk of permanent scarring.
If you ever experience large, painful, or inflamed pimples that don’t heal, it’s essential to consult a dermatologist instead of attempting to treat them at home. Early diagnosis and proper medical intervention are key to restoring healthy skin and preventing future complications.