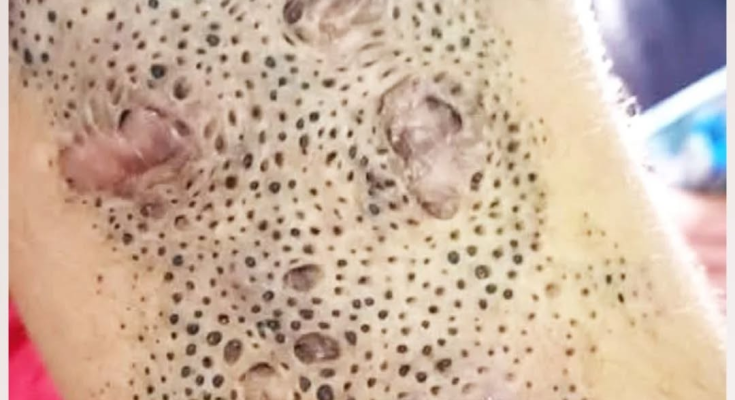
Skin is the body’s largest organ and serves as the first line of defense against bacteria, viruses, and other harmful agents. However, when bacteria find their way into hair follicles or small cuts, infections can develop — leading to painful conditions such as abscesses or folliculitis. The image above depicts a severe case of infected hair follicles, possibly complicated by abscess formation, which requires timely medical attention and proper hygiene care.
What Is a Skin Abscess?
A skin abscess is a collection of pus that forms beneath the surface of the skin due to infection. It often begins when bacteria, most commonly Staphylococcus aureus, enter the skin through small cuts, insect bites, or hair follicles. The body’s immune system responds by sending white blood cells to the infected area, leading to inflammation and the formation of pus — a thick fluid composed of dead tissue, bacteria, and immune cells.
Abscesses can appear anywhere on the body but are most common on areas prone to sweat and friction, such as the armpits, thighs, buttocks, and face.
Causes and Risk Factors
The most common cause of a skin abscess is a bacterial infection, though several other factors can increase the risk:
-
Poor hygiene: Infrequent cleaning or accumulation of sweat and dirt can block hair follicles.
-
Ingrown hairs: When hair grows inward instead of outward, it can trap bacteria under the skin.
-
Compromised immunity: People with diabetes, HIV, or weakened immune systems are more susceptible.
-
Excessive shaving: Repeated irritation from razors can cause micro-cuts, allowing bacteria to enter.
-
Hot and humid climates: These environments encourage bacterial growth and sweating, which may block pores.
Symptoms of a Skin Abscess
Early signs of an abscess or follicular infection include:
-
Redness and tenderness of the skin
-
Swelling and formation of raised bumps
-
Pain or throbbing sensation around the infected area
-
Pus or yellowish discharge
-
Fever or chills in severe cases
In the image, multiple raised bumps and open pores with dark spots are visible, suggesting deep follicular infection and possible scarring from repeated abscesses. Some lesions appear healed, while others are still active, showing signs of pus or dried discharge — an indication that the infection has been recurring or untreated for some time.
Diagnosis
A healthcare provider can diagnose a skin abscess through a simple physical examination. In some cases, a sample of the pus may be taken for laboratory testing to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection. For recurrent infections, blood sugar tests or immune function assessments may be recommended.
Treatment Options
1. Home Remedies (for mild cases):
-
Warm compresses: Applying a warm, moist cloth several times a day helps increase blood flow and promote natural drainage.
-
Good hygiene: Keeping the area clean with mild soap and water reduces bacterial growth.
-
Avoid squeezing: Never try to pop an abscess, as it can spread infection deeper into the skin.
2. Medical Treatment (for moderate to severe cases):
-
Incision and drainage: A doctor may make a small cut to release the pus under sterile conditions.
-
Antibiotics: Oral or topical antibiotics are prescribed to control infection and prevent recurrence.
-
Wound care: Regular cleaning and dressing changes are necessary until the area heals completely.
-
Pain relief: Over-the-counter painkillers can help manage discomfort.
Prevention Tips
-
Maintain personal hygiene by bathing daily and keeping skin dry and clean.
-
Avoid sharing razors, towels, or clothing with others.
-
Shave in the direction of hair growth and use clean blades to prevent follicle irritation.
-
Strengthen your immune system through a balanced diet, exercise, and adequate sleep.
-
Wear loose-fitting clothing to allow your skin to breathe and prevent friction.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical attention immediately if:
-
The abscess grows rapidly or becomes very painful.
-
You develop a fever or swollen lymph nodes.
-
There is spreading redness around the infection site.
-
The infection keeps recurring despite treatment.
Conclusion
A skin abscess or follicular infection may seem like a minor issue at first, but if ignored, it can lead to severe pain, scarring, and even systemic infection. The condition in the image highlights the importance of early diagnosis, cleanliness, and proper treatment. With timely medical care and preventive measures, the skin can heal effectively and regain its healthy appearance.