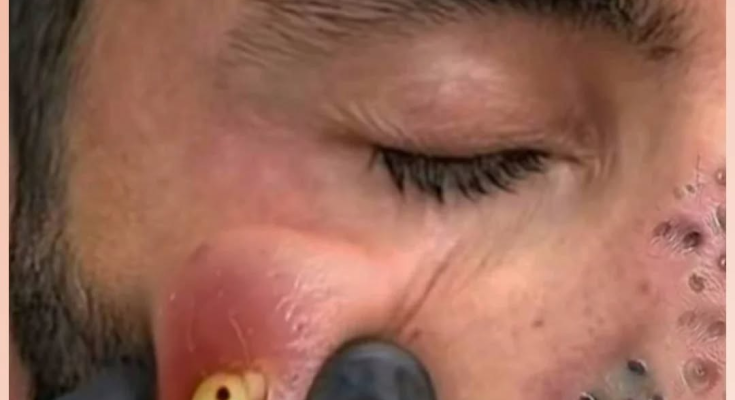
Skin infections can occur anywhere on the body, but when they develop on the face, they are particularly distressing. The face is one of the most visible parts of the body and contains numerous oil glands and hair follicles, which make it more prone to bacterial invasion. The image above shows a severe facial abscess, an infection that has led to the accumulation of pus beneath the skin. Such conditions require careful medical attention to prevent scarring and complications.
What Is a Facial Abscess?
A facial abscess is a painful, swollen lump filled with pus, caused by a bacterial infection under the skin. It often begins as a small pimple or infected hair follicle that worsens over time due to bacterial growth. The infection triggers the immune system to fight off the bacteria, leading to inflammation, redness, and the collection of pus.
In the image, we can see a large swollen area on the cheek filled with yellowish pus and redness — clear indicators of an abscess under pressure. This type of infection is typically caused by Staphylococcus aureus, a common bacterium found on the skin and inside the nose.
Common Causes of Facial Abscesses
-
Bacterial infection: The most frequent cause is Staphylococcus aureus.
-
Blocked hair follicles: When hair follicles are clogged by oil or dead skin, bacteria can multiply inside.
-
Ingrown hairs: Shaving or waxing can cause hair to grow back into the skin, creating irritation and infection.
-
Poor hygiene: Not cleaning the face properly allows sweat, dirt, and oil to build up, promoting bacterial growth.
-
Skin injuries: Cuts, insect bites, or pimples that are squeezed or scratched can allow bacteria to enter the skin.
-
Weak immune system: Conditions like diabetes or chronic illness make infections more likely to occur.
Symptoms of a Facial Abscess
-
Swelling and redness on the face
-
Pain or tenderness at the infected site
-
Formation of a pus-filled lump
-
Warm sensation over the affected area
-
Possible fever or fatigue in severe cases
-
Risk of spreading infection if not treated promptly
In some cases, multiple abscesses or infected pores can appear together, as seen on the nose area in the image, which shows multiple inflamed spots. This suggests a deeper infection of the hair follicles known as furunculosis.
Possible Complications
If left untreated, a facial abscess can lead to serious complications, including:
-
Cellulitis: A deeper skin infection that can spread rapidly.
-
Scarring: Improper drainage or squeezing can leave permanent marks.
-
Spread of infection to the bloodstream: Known as sepsis, which can be life-threatening.
-
Sinus or eye infections: Especially when the abscess is near the nose or eyes.
Therefore, it is critical to seek professional medical treatment instead of attempting to squeeze or drain the abscess at home.
Treatment and Medical Care
1. Medical Drainage
A doctor may perform an incision and drainage procedure under sterile conditions. The area is numbed, and a small incision is made to release the pus, reducing pressure and pain. This allows faster healing and prevents the spread of infection.
2. Antibiotic Therapy
After drainage, antibiotics are prescribed to fight the underlying bacterial infection. Common antibiotics include dicloxacillin, cephalexin, or clindamycin, depending on the bacterial strain and resistance pattern.
3. Proper Wound Care
After drainage, keeping the wound clean and covered is essential. Regular dressing changes and use of prescribed antiseptic ointments prevent reinfection.
4. Home Care and Supportive Remedies
-
Apply warm compresses to promote natural drainage.
-
Avoid touching or squeezing the abscess.
-
Keep facial skin clean using mild, non-comedogenic cleansers.
-
Stay hydrated and maintain good nutrition to support healing.
Prevention Tips
To reduce the risk of developing facial abscesses or follicular infections, follow these preventive steps:
-
Maintain facial hygiene by washing the face twice daily with mild cleansers.
-
Avoid sharing razors, towels, or cosmetics.
-
Disinfect shaving tools and change blades frequently.
-
Avoid popping pimples or blackheads, as this can push bacteria deeper into the skin.
-
Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals that strengthen the immune system.
-
Seek early treatment for any persistent skin irritation, pimples, or cysts.
When to See a Doctor
You should seek medical care if:
-
The swelling increases rapidly or becomes very painful.
-
You notice pus accumulation under the skin.
-
The infection spreads to other parts of the face.
-
You experience fever, chills, or fatigue.
-
The abscess recurs after previous treatment.
Conclusion
A facial abscess is more than just a simple skin problem — it’s a sign of bacterial infection that needs immediate medical attention. While home remedies can help mild cases, deep or large abscesses like the one in the image must be treated by a healthcare professional to avoid serious complications. Proper hygiene, early intervention, and avoiding self-extraction are key to maintaining healthy, infection-free skin.