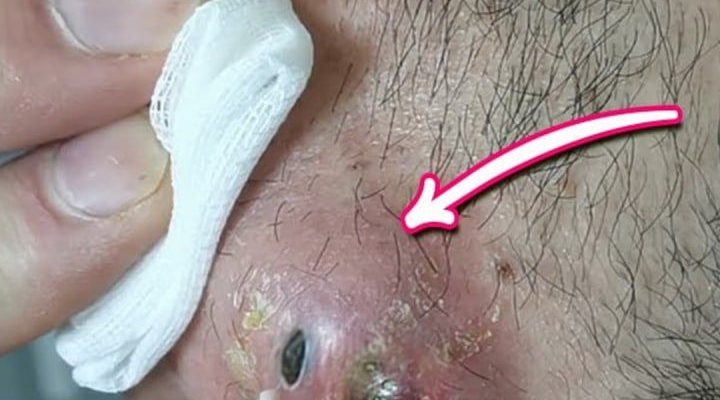
A facial abscess is a painful, swollen bump filled with pus that develops beneath the skin due to bacterial infection. It often appears red, tender, and warm to the touch, causing both discomfort and cosmetic concern. If left untreated, a facial abscess can spread, leading to severe infection, scarring, or tissue damage. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help you heal quickly and prevent future outbreaks.
What Is a Facial Abscess?
A facial abscess forms when bacteria infect a hair follicle or damaged skin tissue. The immune system reacts by sending white blood cells to fight the infection, leading to pus buildup. This creates a visible lump that may increase in size and pain over time. Abscesses commonly develop on the cheeks, jawline, or around the mouth, where skin pores and hair follicles are more prone to bacterial blockage.
Main Causes of Facial Abscesses
Facial abscesses usually result from bacterial infections, most often caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Common causes include:
-
Poor skin hygiene and unclean shaving tools
-
Clogged pores or infected acne lesions
-
Ingrown hairs or small skin injuries
-
Weakened immune system or underlying health issues
-
Excessive sweating and exposure to dirt or pollution
Maintaining proper facial hygiene and avoiding skin trauma can significantly reduce your risk.
Common Symptoms of a Facial Abscess
Early detection of an abscess can prevent serious complications. Typical symptoms include:
-
Painful red lump under the skin
-
Swelling and warmth in the affected area
-
Visible pus or drainage
-
Skin tenderness and inflammation
-
Fever or fatigue in severe infections
If you notice these signs, seek medical or dermatological advice immediately to avoid worsening infection.
How to Treat a Facial Abscess
The most effective treatment for a facial abscess is incision and drainage, performed by a qualified healthcare provider. Here’s what typically happens during the procedure:
-
The affected area is cleaned and disinfected.
-
Local anesthesia is applied to numb the skin.
-
A small incision is made to drain the pus.
-
The wound is cleaned, and antibiotics may be prescribed.
-
A sterile dressing is applied to promote healing.
Never attempt to pop or squeeze an abscess at home, as this can spread the infection and cause deeper tissue damage.
Aftercare and Home Remedies
Post-treatment care is crucial for quick recovery and preventing recurrence. Follow these tips:
-
Keep the wound clean and covered.
-
Use prescribed antibiotics or ointments.
-
Avoid touching or scratching the healing area.
-
Apply a warm compress to reduce pain and swelling.
-
Stay hydrated and maintain a healthy diet for skin repair.
Natural remedies such as tea tree oil (antibacterial), aloe vera (soothing), and turmeric (anti-inflammatory) may also help support healing—but only after consulting your doctor.
Preventing Future Facial Abscesses
To prevent future outbreaks:
-
Wash your face twice daily with mild cleanser.
-
Shave with clean, disinfected tools.
-
Avoid picking pimples or touching your face unnecessarily.
-
Manage underlying health conditions like diabetes or acne.
Conclusion
A facial abscess can be painful and distressing, but with early diagnosis and proper treatment, healing is quick and effective. If you notice swelling, redness, or pus-filled bumps on your face, visit a healthcare provider immediately. Practicing good facial hygiene, following aftercare steps, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are the best ways to prevent abscess recurrence and keep your skin healthy and glowing.