-
Discover the causes, symptoms, and treatments for severe facial abscesses and cystic skin infections. Learn how to identify, treat, and prevent recurring abscesses on the face safely and effectively.
What Is a Facial Abscess?
A facial abscess is a serious bacterial skin infection that forms when bacteria invade the deeper layers of the skin, causing inflammation, pus buildup, and swelling. It usually presents as red, painful bumps that may fill with pus or fluid. In advanced cases, abscesses can cluster together, causing discomfort and significant tissue damage.
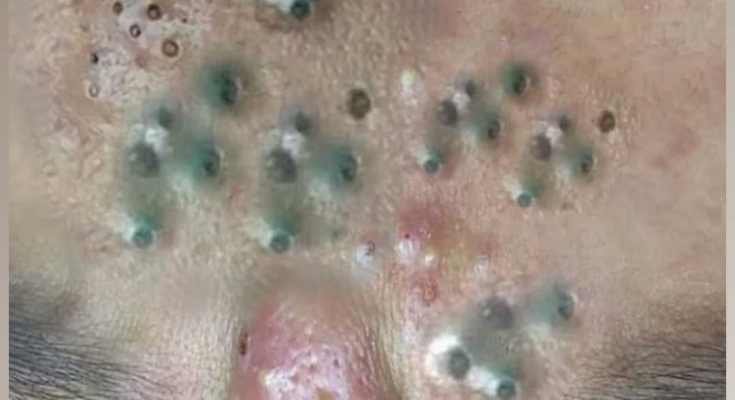
The image above shows a severe case of multiple abscesses affecting the forehead and nasal area — a condition that needs urgent medical care. Without timely treatment, infections like these may spread deeper or even cause systemic complications.
Main Causes of Facial Abscesses
Several factors contribute to abscess formation, including bacterial infection, poor hygiene, or blocked pores. Below are the most common causes:
-
Bacterial Infection:
The most frequent cause is Staphylococcus aureus, including resistant strains like MRSA (Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus). -
Blocked Sebaceous Glands:
When oil glands or hair follicles become clogged with dead skin and bacteria, infection can develop beneath the surface. -
Poor Facial Hygiene:
Sweat, dirt, and oil accumulation encourage bacterial growth, leading to infections. -
Weak Immune System:
Individuals with diabetes, chronic illnesses, or stress have a reduced ability to fight bacterial invasion. -
Skin Trauma or Injury:
Cuts, insect bites, or shaving wounds can create openings for bacteria to enter the skin.
Symptoms of a Severe Facial Abscess
Recognizing symptoms early is crucial for effective treatment. Typical signs include:
-
Painful, red, and swollen skin areas
-
Pus-filled bumps or cysts
-
A warm sensation over infected areas
-
Tenderness and pressure pain
-
Fever and fatigue in serious cases
-
Multiple abscess clusters that may merge together
Diagnosis and Medical Examination
A dermatologist or healthcare provider can diagnose facial abscesses through:
-
Physical Examination: Checking for swelling, redness, and pus.
-
Pus Culture Tests: Identifying the specific bacteria causing the infection.
-
Blood Tests: To detect the severity and any spread of infection.
Treatment Options for Facial Abscesses
Treating a facial abscess depends on the infection’s severity. Here are common medical and home-based approaches:
1. Professional Drainage
Doctors may perform an incision and drainage procedure under sterile conditions to release trapped pus and speed up healing. This step should never be done at home.
2. Antibiotic Therapy
Prescription antibiotics — either topical or oral — are used to combat bacterial growth. In severe cases, intravenous antibiotics may be necessary.
3. Pain Management
Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medicines help reduce swelling and discomfort.
4. Proper Wound Care
Keeping the affected area clean, dry, and covered with sterile dressings promotes healing and prevents reinfection.
5. Avoid Self-Extraction
Never squeeze or pop abscesses. Doing so can spread bacteria, cause deeper infection, and lead to scarring.
Home Remedies and Preventive Tips
To prevent abscess formation or recurrence:
-
Wash your face daily with a mild antibacterial cleanser.
-
Avoid using harsh skincare products that irritate the skin.
-
Keep your pillowcases and towels clean.
-
Do not share razors, towels, or cosmetics.
-
Strengthen your immune system through proper nutrition and hydration.
-
Visit a dermatologist if abscesses appear frequently.
When to See a Doctor
Immediate medical attention is necessary if you experience:
-
Increasing pain and swelling
-
Fever, fatigue, or spreading redness
-
Pus drainage that smells foul
-
Multiple abscesses forming in clusters
Ignoring severe abscesses may lead to deeper infections, scarring, or complications such as cellulitis.
Conclusion
A facial abscess is more than just a skin problem — it’s a bacterial infection that can escalate quickly without proper care. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options helps prevent serious health issues. If you notice severe or recurring lesions, consult a healthcare professional immediately. Early diagnosis and proper treatment are the keys to full recovery and healthy skin.
-